What is a kyphoplasty?
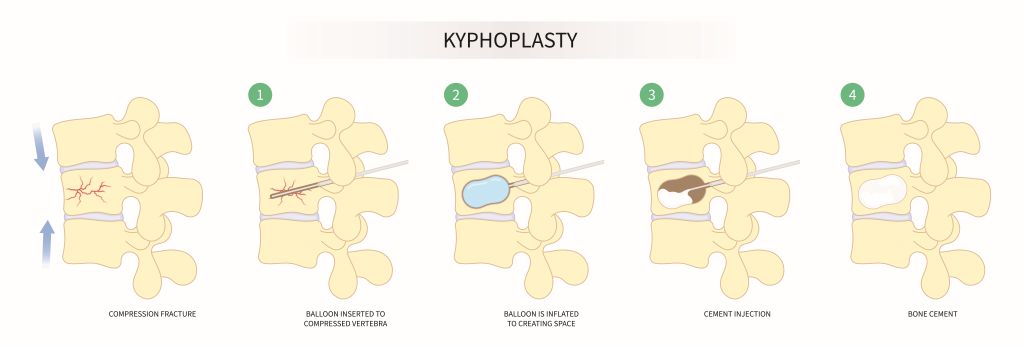
Kyphoplasty is a medical procedure used to treat vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) in the spine. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves the injection of bone cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize the bone and alleviate pain.
During a kyphoplasty, a small incision is made in the back and a narrow tube is inserted into the fractured vertebra under X-ray guidance. A small balloon is then inserted through the tube and inflated to create a cavity within the vertebra. The cement-like material is then injected into the cavity, filling it and stabilizing the bone.
What is a compression fracture?
Compression fractures of the spine occur when one or more vertebrae (bones of the spine) become compressed or collapsed. This can cause pain, reduced mobility, and other symptoms.
The most common cause of compression fractures of the spine is osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and makes them more prone to fractures. Other causes include trauma to the spine, such as from a fall or car accident, and cancer that has spread to the bones of the spine.
When is kyphoplasty used to treat compression fractures?
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to treat compression fractures of the spine, particularly those caused by osteoporosis. It is typically recommended when other conservative treatments, such as pain medications and bracing, have failed to provide adequate relief.
Some of the specific indications for using kyphoplasty to treat a compression fracture include:
- Severe pain: Patients with compression fractures of the spine may experience severe pain that does not respond to other treatments.
- Limited mobility: Compression fractures can also lead to a reduction in mobility and may limit the ability to perform daily activities.
- Presence of osteoporosis: Patients with osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, are at higher risk of developing compression fractures of the spine.
- Recent fracture: If a compression fracture of the spine is recent, kyphoplasty may be recommended to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of complications.
- Fracture in a weight-bearing area: If the compression fracture is located in a weight-bearing area of the spine, such as the lumbar region, kyphoplasty may be recommended to prevent further damage and improve mobility.
What is the difference between a kyphoplasty and a vertebroplasty?
Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty are both minimally invasive surgical procedures used to treat vertebral compression fractures, but there are some differences between the two procedures.
Vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty involves the injection of a special cement-like material directly into the fractured vertebra to stabilize it and provide pain relief. During the procedure, a small needle is inserted into the vertebra and the cement-like material is injected. Vertebroplasty does not involve the use of a balloon or any other tools to restore the height of the vertebra.
Kyphoplasty
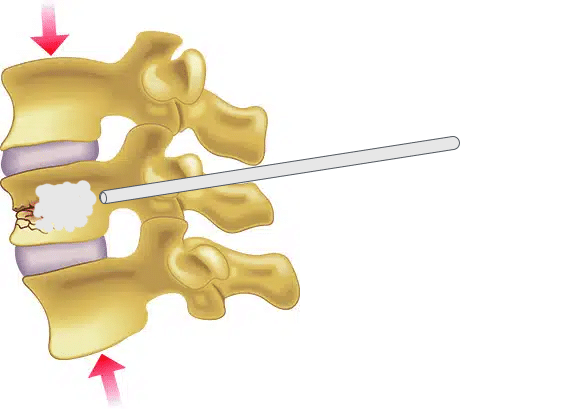
Kyphoplasty, on the other hand, involves the use of a small balloon to create a space in the fractured vertebra before the cement-like material is injected. The balloon is inserted into the vertebra and inflated, which helps to restore the height of the vertebra and create a cavity for the cement-like material. The balloon is then removed and the cement-like material is injected into the cavity.
One advantage of kyphoplasty over vertebroplasty is that it may help to restore the height of the compressed vertebra, which can improve spinal alignment and reduce the risk of developing a spinal deformity such as kyphosis (a forward curvature of the spine).

What can I expect during the procedure?
If you are scheduled to undergo a kyphoplasty procedure, here is a general overview of what you can expect
- Preparation: You will be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie face down on the operating table. The medical staff will clean and sterilize the area where the incision will be made. You will be given anesthesia to keep you comfortable and still during the procedure.
- Insertion of the cannula: Using X-ray guidance, the surgeon will insert a narrow tube called a cannula into the affected vertebra through a small incision in your back.
- Balloon insertion: Once the cannula is in place, the surgeon will insert a small balloon through it and into the affected vertebra. The balloon is then inflated to create a cavity in the center of the vertebra.
- Cement injection: Once the cavity is created, the surgeon will remove the balloon and use a special device to inject a cement-like material called polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) into the cavity. The cement hardens quickly and stabilizes the vertebra.
- Recovery: You will be taken to a recovery area where you will be monitored for a few hours. You may be allowed to go home on the same day of the procedure or may need to stay in the hospital overnight for observation.
The procedure generally takes about 1-2 hours to complete
What is the recovery time after a kyphoplasty?
Most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few days following the procedure however recovery time after can vary depending on the individual patient and the extent of the procedure.
Patients may be advised to rest and limit activity for the first 24-48 hours after the procedure and avoid strenuous activity, heavy lifting, or bending at the waist for at least several weeks after the procedure.
What are the risks?
As with any medical procedure, kyphoplasty carries some risks and potential complications. Some of the risks of kyphoplasty include:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the injection site or in the surrounding tissues.
- Bleeding: There is a small risk of bleeding during or after the procedure, particularly if the patient is taking blood-thinning medications.
- Nerve damage: There is a risk of nerve damage during the procedure, which could result in pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
- Cement leakage: There is a risk that the cement-like material used to stabilize the vertebra could leak into surrounding tissues, which could cause pain or other complications.
- Allergic reaction: Some patients may have an allergic reaction to the materials used during the procedure.
Is kyphoplasty right for me?
Whether or not kyphoplasty is the right treatment option for you will depend on a variety of factors, including the severity and location of your compression fracture, your overall health, and your preferences and goals for treatment. It is important to discuss your options with a qualified healthcare provider who can evaluate your individual case and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for you.